Decoding Your Hormones: What to Do About Imbalance
Understanding Your Body's Chemical Messengers

Hormone imbalance treatment addresses conditions where your body produces too much or too little of specific hormones, restoring balance through medical therapies, lifestyle changes, or both.
Quick Overview of Treatment Options:
| Treatment Category | Common Approaches |
|---|---|
| Medical Treatments | Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), thyroid medication, anti-androgen drugs, insulin-sensitizing medications |
| Natural Approaches | Herbal supplements, acupuncture (under medical guidance) |
| Lifestyle Changes | Balanced nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, quality sleep |
| Specialized Care | Bioidentical hormone optimization, fertility treatments, individualized protocols |
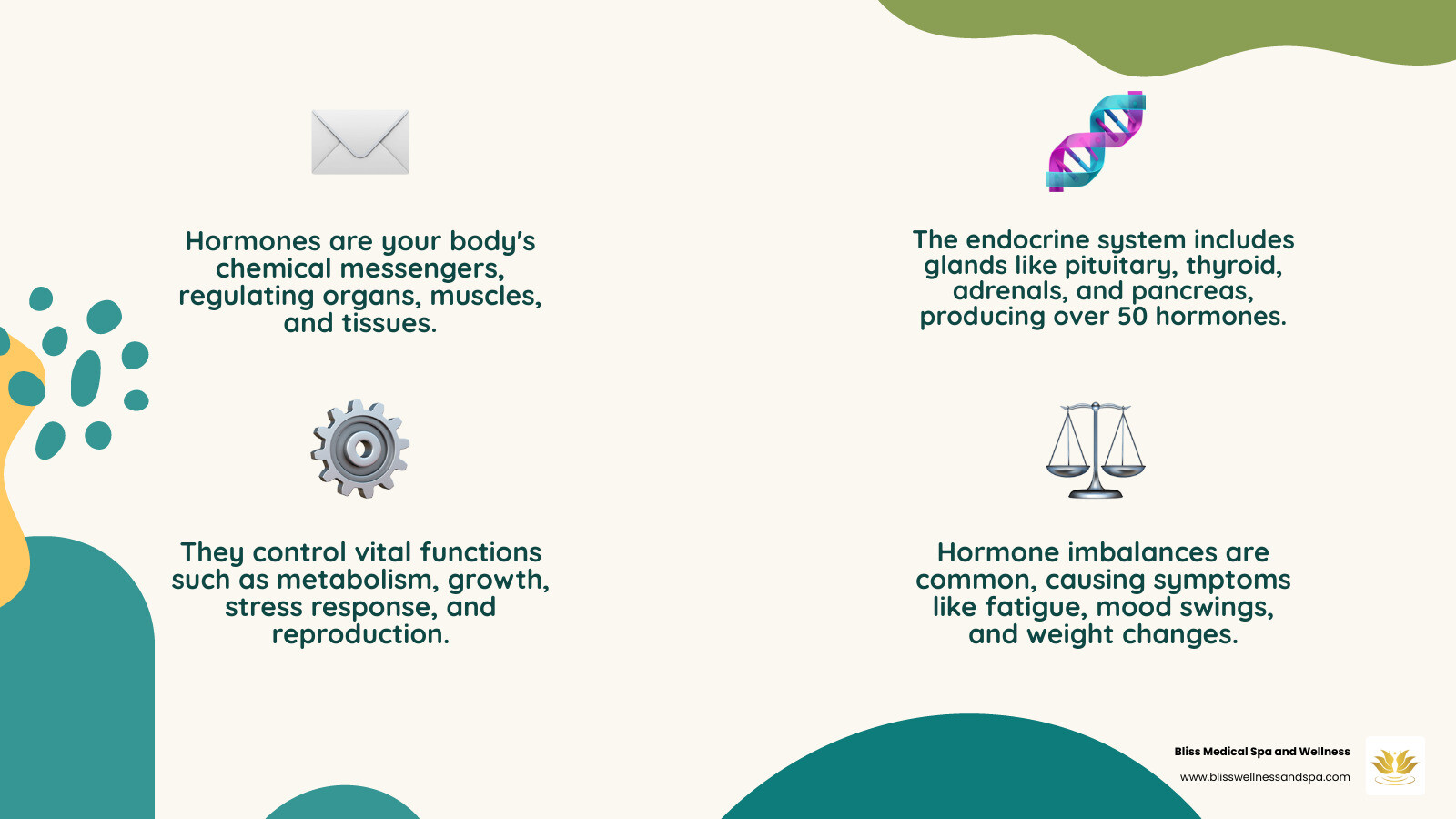
Hormones are your body's chemical messengers, traveling through your bloodstream to tell organs and tissues what to do. Over 50 different hormones work together as part of your endocrine system.
When these hormones fall out of balance, you might experience fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, or sleep problems. Hormone imbalances are remarkably common, affecting people at all life stages.
The good news is that most imbalances are treatable once properly diagnosed. Understanding the cause—whether it's stress, a medical condition like thyroid disease, or natural life changes—is the first step toward finding an effective solution.
As Dawn Dewane, a board-certified Family Nurse Practitioner at Bliss Medical Spa and Wellness, I specialize in bioidentical hormone optimization and longevity medicine. I've helped countless clients restore their energy and vitality by creating personalized treatment plans that address root causes, not just symptoms.
Understanding the Signs: Symptoms and Causes of Hormonal Imbalance
When hormones are imbalanced, our bodies send signals that can impact daily life. Recognizing these symptoms is the first step toward getting help.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Imbalances cause a wide array of overlapping physical and mental symptoms, making professional diagnosis essential.
- Weight Changes: Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight can be a sign. Conditions like hypothyroidism or Cushing's syndrome can cause weight gain, while some imbalances lead to weight loss.
- Fatigue: Chronic fatigue not relieved by rest is a common complaint linked to thyroid issues, adrenal insufficiency, or other hormonal disruptions.
- Mood Swings: Hormones regulate mood, so imbalances can lead to anxiety, depression, or irritability. For example, thyroid issues or low estrogen can affect mood.
- Skin Problems: Hormonal fluctuations affect skin health, causing acne (especially adult acne), dry skin, or dark patches (hyperpigmentation).
- Hair Loss or Excessive Growth: Thinning hair is often associated with thyroid issues or low sex hormones. Excessive hair growth (hirsutism) can indicate high levels of male hormones, as seen in PCOS.
- Sleep Issues: Difficulty sleeping, insomnia, or night sweats can signal hormonal disruption, commonly seen during menopause due to fluctuating estrogen.
- Libido Changes: A decreased sex drive is a frequent symptom. Low testosterone in men and low estrogen in women can reduce libido and cause related issues like erectile dysfunction or vaginal dryness.
- Digestive Problems: Hormones like estrogen and progesterone influence gut function, and imbalances can lead to constipation, diarrhea, or symptoms associated with IBS.
Here are some symptoms specific to men versus women:
- Symptoms Often More Prominent in Women:
- Heavy, irregular, or painful periods
- Osteoporosis (especially with low estrogen)
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Vaginal dryness or atrophy
- Increased urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Breast tenderness
- Infertility and anovulation
- Symptoms Often More Prominent in Men:
- Decreased body hair
- Erectile dysfunction
- Gynecomastia (enlarged breast tissue)
- Infertility
- Loss of muscle mass
The Primary Causes Behind the Imbalance
The causes of hormonal imbalances range from natural life stages to medical conditions and lifestyle factors, which are key to effective hormone imbalance treatment.
- Medical Conditions: Many underlying health issues can disrupt your hormones.
- Diabetes: The most common endocrine condition in the U.S., involving insulin issues.
- Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidism (underactive) or hyperthyroidism (overactive) affect metabolism, energy, and mood. Up to 50% of people treated for head and neck cancer with radiation develop hypothyroidism.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A common disorder and leading cause of female infertility, involving an imbalance of reproductive hormones.
- Adrenal and Pituitary Conditions: These include Adrenal Insufficiency (Addison's disease), Cushing's Syndrome (excess cortisol), and Hypopituitarism (pituitary gland underproduction).
- Other Conditions: Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI), ovarian cancer, anorexia nervosa, and tumors on endocrine glands can all disrupt hormone function.
- Stress and Cortisol: Chronic stress releases excess cortisol, the "stress hormone," which negatively impacts sex and thyroid hormones. Stress management is a critical part of treatment.
- Poor Diet and Nutritional Deficiencies: A diet high in processed foods and sugar can cause inflammation and disrupt hormone production. Nutrient deficiencies also impair hormone function.
- Lack of Exercise: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to insulin resistance and other imbalances.
- Aging Process: Hormone levels naturally change with age during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause.
- External Factors:
- Medications: Certain drugs, like hormonal birth control or cancer treatments, can impact hormone levels. Accidental damage to endocrine glands during surgery can also cause deficiencies; approximately 75% of hypoparathyroidism cases are from accidental damage to your parathyroid glands from neck or thyroid surgery.
- Toxins and Environmental Chemicals: Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals in plastics, pesticides, and cleaners can interfere with hormone function.
For more detailed information on the various causes of hormonal imbalances, we often refer to scientific research and trusted medical sources. You can find more insights on this topic by exploring scientific research on causes of imbalance.
Getting a Diagnosis: How Doctors Identify Hormone Imbalances
If you suspect a hormonal imbalance, a professional diagnosis is the essential next step for effective hormone imbalance treatment. At Bliss Medical Spa and Wellness, we take a thorough, personalized approach to understanding your hormonal profile.
The Consultation and Evaluation Process
Our journey begins with a comprehensive consultation to form a complete picture of your health.
- Discussing Symptoms: We'll ask you to describe all your symptoms, their timing, and severity to help connect the dots.
- Medical History Review: We review your personal and family medical history, current medications, and lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and stress.
- Physical Exam: A physical exam helps identify outward signs of imbalance. For women, a pelvic exam may also be performed.
- When to Seek Medical Attention: We encourage you to seek medical attention for any new, persistent, or worsening symptoms that impact your quality of life. Early detection makes a significant difference.
Key Diagnostic Tests for Hormone Imbalance Treatment
After the initial evaluation, we may recommend specific diagnostic tests to measure your hormone levels.
- Blood Tests: These are the most common diagnostic tool. Blood tests can measure levels of:
- Estrogen and Progesterone: For female reproductive health (PCOS, menopause).
- Testosterone: Important for both men and women. Levels in men show a circadian rhythm, peaking in the morning.
- Thyroid Hormones (TSH, T4, fT4): To diagnose hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
- Cortisol: The stress hormone. We often measure serum cortisol at 8–9 am. A level below 3 μg/dL suggests insufficiency, while above 15 μg/dL likely rules it out. Levels in between may require further testing. More information on cortisol testing can be found at Information on Cortisol Testing.
- Insulin: To diagnose diabetes and assess insulin resistance.
- FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone) and LH (Luteinizing Hormone): For reproductive health and diagnosing conditions like hypogonadism.
- IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 1) and Prolactin (PRL): To assess growth hormone and prolactin-related disorders.
- Saliva Tests: Can be used to measure free, active levels of certain steroid hormones.
- Urine Tests: A 24-hour urine collection can measure hormone metabolites, offering a view of hormone production over a full day. For example, urine osmolarity is used in diagnosing diabetes insipidus.
- Dynamic or Stimulation Tests: These tests measure hormone levels before and after administering a substance to stimulate or suppress production, such as a corticotropin stimulation test for adrenal insufficiency.
- Imaging Tests:
- Ultrasound: To examine ovaries (for PCOS), thyroid, or adrenal glands.
- MRI or CT Scans: To visualize the pituitary or other endocrine glands if a tumor is suspected.
- Thyroid Scan: To assess thyroid nodules or function.
- Biopsy: In rare cases, a biopsy may be needed to determine the nature of a growth or tumor.
These diagnostic steps allow us to identify the specific imbalance and develop an effective, customized hormone imbalance treatment plan for you.
A Guide to Hormone Imbalance Treatment Options
Once an imbalance is identified, we create a personalized hormone imbalance treatment plan. Our approach at Bliss Medical Spa and Wellness combines medical therapies with lifestyle adjustments for optimal health.
Medical and Therapeutic Treatments
Medical treatments are often necessary to restore hormonal balance, especially in cases of significant deficiencies or excesses.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): A cornerstone treatment for hormone deficiencies, HRT supplements the body with hormones to bring levels into a healthy range.
- For women, HRT can alleviate menopausal symptoms and help prevent osteoporosis.
- For men with low testosterone, it can improve libido, energy, and muscle mass.
- For hypopituitarism, HRT replaces missing pituitary hormones like cortisol, thyroid hormone, and growth hormone.
- Bioidentical Hormone Optimization: At Bliss Medical Spa and Wellness, we specialize in using hormones chemically identical to those your body produces. This personalized approach, involving estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone, aims for a more natural response and optimal results.
- Thyroid Hormone Therapy: For hypothyroidism, synthetic thyroid hormone (Levothyroxine) is prescribed to restore normal thyroid function and energy levels.
- Anti-Androgen Medications: For conditions with excess male hormones (androgens), like PCOS, these drugs can reduce symptoms like excessive hair growth and acne.
- Metformin for Insulin Resistance: Prescribed for conditions like PCOS or Type 2 Diabetes, Metformin improves the body's insulin sensitivity and helps manage blood sugar.
- Fertility Medications: For hormonal infertility, medications like Clomiphene can stimulate ovulation. In some cases, assisted reproductive technologies like in-vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended.
- Medications for Excess Hormones: When the body produces too much of a hormone, medications can suppress its production. For example, dopamine agonists treat prolactinomas.
- Surgery or Radiation Therapy: If a tumor is causing the imbalance, surgery or radiation may be necessary to remove or shrink it.
Our team follows the latest evidence-based practices. For more information, you can refer to sources like the Clinical Practice Guidelines from the Endocrine Society.
Exploring Natural Hormone Imbalance Treatment
While medical intervention is often essential, some people explore natural approaches. It's crucial to discuss any natural hormone imbalance treatment with your provider to ensure safety, as few supplements have strong scientific proof.
- Herbal Supplements: Herbs like black cohosh, chasteberry, and maca root are sometimes used for hormonal symptoms. However, scientific evidence for their efficacy is often limited. We strongly advise against self-prescribing.
- Importance of Medical Guidance: Always consult with your healthcare provider before trying a natural approach. They can assess risks, check for medication interactions, and ensure your overall treatment plan is safe and cohesive.
Lifestyle Strategies for Managing Hormonal Health
Daily choices profoundly impact hormonal balance. Healthy lifestyle strategies are a powerful part of any hormone imbalance treatment plan, working with medical therapies to optimize well-being.
The Role of Diet and Nutrition
What we eat directly influences our endocrine function. A balanced, nutrient-rich diet is fundamental.
- Balanced Diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods to provide building blocks for hormones and maintain stable blood sugar.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate fats from sources like fatty fish, avocados, and nuts, which are crucial for hormone production.
- Lean Protein: Include adequate lean protein in every meal to regulate appetite hormones.
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support gut health, which is linked to hormone metabolism.
- Limiting Sugar and Reducing Processed Foods: Excess sugar and processed foods can cause insulin spikes and inflammation. Reducing them improves insulin sensitivity.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential for hormone transport and cellular communication.
- Sunlight Exposure: Adequate sunlight helps regulate vitamin D levels, which acts as a hormone in the body.
- Avoiding Toxins: Minimize exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals in some cleaners, pesticides, and certain non-stick cookware.
How Exercise Regulates Your Hormones
Regular physical activity is a potent regulator of hormonal health, and evidence suggests it can improve insulin resistance.
- Stress Reduction: Exercise is a fantastic stress reliever, helping to lower cortisol levels.
- Improving Insulin Sensitivity: Regular exercise can significantly reduce insulin levels and increase insulin sensitivity, helping cells use blood sugar for energy.
- Weight Management: Exercise supports healthy weight, which positively influences hormones like estrogen and leptin.
- Boosting Hormone Receptor Sensitivity: Exercise increases the sensitivity of hormone receptors, enhancing hormonal signals.
We recommend incorporating a variety of exercises into your routine:
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods.
- Strength Training: Builds muscle mass, which improves insulin sensitivity.
- Cardio (Aerobic Exercise): Activities like jogging, swimming, or cycling.
- Even Walking: Regular walking can increase key hormone levels, potentially improving strength and quality of life.
Managing Stress and Its Impact on Mental Health
Stress directly impacts our hormones, and vice versa. Managing it is key.
- Cortisol Regulation: Chronic stress keeps cortisol levels high, which can disrupt thyroid and sex hormone balance. Effective stress management is a cornerstone of hormone imbalance treatment.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like mindfulness and meditation can calm the nervous system and reduce cortisol.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritizing 7-9 hours of quality sleep is vital, as sleep deprivation impacts cortisol, growth hormone, and insulin.
- Connection Between Hormones and Mood: Hormonal imbalances can cause anxiety and depression. Addressing the imbalance often leads to significant improvements in mental well-being.
Long-Term Health and Hormonal Changes Through Life
Our hormones shift throughout our lives. Understanding these changes and the long-term consequences of untreated imbalances is vital for proactive health management.
Hormones Across a Woman's Lifespan
Women experience significant hormonal fluctuations, each bringing unique challenges.
- Puberty: Most females enter puberty between ages 8 and 13. This phase is marked by a surge in sex hormones, leading to physical development and the start of menstrual cycles.
- Menstrual Cycle: This monthly rhythm (typically 25-36 days) involves fluctuations of estrogen and progesterone. Imbalances can lead to irregular periods or conditions like PCOS.
- Pregnancy: This is a period of profound hormonal shifts, with human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), progesterone, and estrogen levels soaring to support fetal development.
- Perimenopause and Menopause: Menopause is reached 12 months after a woman's last period (usually around age 50). The transition, perimenopause, can last for years. Both stages involve declining estrogen and progesterone, leading to symptoms like hot flashes, mood swings, and weight gain.
Here's a comparison of hormonal changes and symptoms across key life stages for women:
| Life Stage | Key Hormonal Changes | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Puberty | Rising Estrogen, Progesterone, Testosterone | Breast development, pubic and underarm hair growth, growth spurts, acne, mood swings, onset of menstruation. |
| Pregnancy | High hCG, Estrogen, Progesterone, Prolactin | Morning sickness, fatigue, breast tenderness, weight gain, mood changes, increased appetite, changes in skin and hair (e.g., thicker hair due to increased progesterone). |
| Menopause | Declining Estrogen, Progesterone | Hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, decreased libido, mood swings, sleep disturbances, weight gain (slowing metabolism), thinning hair, dry skin, increased risk of osteoporosis and cardiovascular issues. |
Potential Consequences of Untreated Imbalances
Ignoring hormonal imbalances can lead to serious long-term health consequences, which is why proactive hormone imbalance treatment is so important.
- Infertility: Hormonal imbalances, like PCOS, are a leading cause of infertility in females. Low testosterone can contribute to infertility in men.
- Osteoporosis: Low estrogen, especially with early menopause, increases the risk of osteoporosis. High glucocorticoid exposure can also negatively impact bone health.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Untreated imbalances can increase heart disease risk. Early menopause without estrogen replacement, thyroid issues, and low testosterone in men are all risk factors.
- Diabetes: As the most common endocrine condition, diabetes is a direct result of insulin imbalance. Other hormonal issues, like high cortisol, can also increase diabetes risk.
- Obesity: Conditions like hypothyroidism and PCOS can lead to weight gain and obesity, which can worsen hormonal imbalances.
- Mental Health Disorders: Chronic imbalances can contribute to persistent anxiety, depression, and severe mood swings.
- Other Conditions: Untreated hypopituitarism can lead to increased morbidity and premature mortality, often due to cardiovascular disease.
When to See a Doctor: Consult with us for any new, persistent, or worsening symptoms. Early diagnosis and a custom hormone imbalance treatment plan can prevent long-term complications and help you regain control of your health.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Hormonal Wellness
Understanding and addressing hormonal imbalances is a journey toward reclaiming your health and vitality. We've explored the diverse symptoms, underlying causes, diagnostic methods, and comprehensive hormone imbalance treatment options available to you.
Hormones are powerful chemical messengers that influence virtually every aspect of your well-being. When they're out of balance, the effects can be widespread, impacting your energy, mood, weight, sleep, and overall quality of life.
The good news is that you don't have to steer these challenges alone. With accurate diagnosis and a personalized approach, most hormonal imbalances can be effectively managed. This often involves a combination of medical therapies, such as hormone replacement or specific medications, alongside powerful lifestyle strategies including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and effective stress management.
At Bliss Medical Spa and Wellness in Phoenix, AZ, and Glendale, AZ, we are dedicated to providing personalized care that addresses the root causes of your hormonal imbalances. Our approach is designed to empower you with knowledge and equip you with a custom plan to optimize your hormonal health. We believe in proactive health management, helping you feel your best today and for years to come.
Take the first step towards hormonal harmony. Learn more about how we can support your journey to wellness by exploring More info about our wellness services.


